
When using the Windows operating system, some users may notice that Antimalware Service Executable (MsMpEng.exe) consumes a significant amount of memory and CPU resources, impacting system performance and slowing down the computer. This article will introduce several practical methods to reduce its memory usage and improve overall system efficiency.
1. Check for Device Driver Updates
Outdated or corrupted drivers may cause high memory usage by Antimalware Service Executable. Regularly checking and updating device drivers can effectively resolve this issue. Driver Sentry is recommended for automatically detecting and updating drivers, saving time and reducing the risk of downloading or installing incorrect drivers.
Click the download button to get the latest version of Driver Sentry. After installation, open the software and click "Scan".

Once the scan is complete, it will display a list of drivers that need installation or updates. Find the required drivers in the results list and click the "Upgrade" button.
After updating, it is recommended to restart the computer to ensure the newly installed drivers function properly.
2. Adjust Windows Defender Exclusions
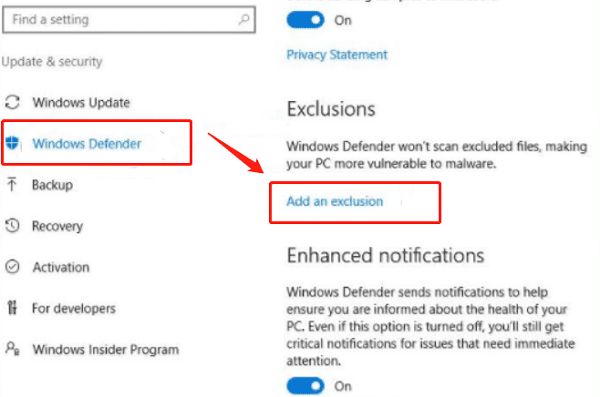
Press Win + I to open Settings, then go to "Update & Security".
Find "Windows Defender" and click "Add an exclusion" under Exclusions.
Select "Exclude .exe, .com, or .scr process" from the process list.
Type "MsMpEng.exe" and click OK to apply the changes.
3. Disable Windows Defender's Scheduled Scans
Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog, type "taskschd.msc", and press Enter.
Navigate to "Task Scheduler Library" > "Microsoft" > "Windows", locate and expand "Windows Defender", then double-click "Windows Defender Scheduled Scan".
In the Properties window, uncheck "Run with highest privileges".

Go to the "Conditions" tab, uncheck all options, and click OK to save the changes.
4. Disable Windows Defender via the Registry
Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
Type "regedit" and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
In the navigation panel, go to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender
Locate DisableAntiSpyware, then set its value to "1".

Note: If DisableAntiSpyware does not exist, right-click on an empty area in the Registry Editor, select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value, name it DisableAntiSpyware, then double-click it and set the value to "1".
5. Disable Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling
Press Win + I to open Settings.
Navigate to "System" > "Display", then scroll down to "Graphics Settings".
Under "Graphics Performance Preference", find Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling.
Turn off this feature (if already off, try turning it on and then off again).
Restart the computer to apply changes, then check if the issue persists.
6. Check for Windows Updates
Press Win + I to open Settings.
Go to "Update & Security" > "Windows Update".
Click "Check for updates", and if updates are available, click "Download and install".
Restart the computer and check if the issue is resolved.
By following these methods, most users can effectively reduce the memory usage of the Antimalware Service Executable process, ensuring smoother system performance. If the problem persists, consider seeking professional technical support or upgrading hardware.
See also:
Fix Keyboard That Can't Type Numbers
Solve the Keyboard Not Typing Letters Issue