
Many Windows users may experience persistent crashes, impacting computer performance. This article offers effective solutions to help resolve the issue and restore normal operation.
1. Check Connections
Unplug all external devices (such as USB devices, printers, external monitors, etc.), leaving only essential devices (such as the keyboard and mouse).
Ensure that the power cable is securely connected and that the power supply is working correctly.
Confirm that the monitor's power and signal cables are functioning properly to avoid mistakenly assuming a system crash due to display issues.
2. Check Drivers
Outdated or incompatible drivers may cause Windows to crash. Make sure all hardware drivers are up to date. It is recommended to use Driver Sentry to automatically detect and update drivers, saving time and avoiding the risk of downloading or installing incorrect drivers.
Click the download button to get the latest version of Driver Sentry. After installation, open the software and click "Scan".

After the scan is complete, it will show the drivers that need to be installed or updated. Find the necessary drivers and click the "Upgrade" button.
After updating, it is recommended to restart your computer to ensure the new drivers are applied properly.
3. Boot into Safe Mode
Hold the power button until the computer shuts down completely.
Press the power button to turn the computer back on.
When the computer begins to start and the manufacturer's logo appears, press and hold the power button again to force the computer to shut down.
Repeat this process 3 times, then press the power button to enter the Windows Repair menu.
Select "Troubleshoot" > "Advanced options" > "Startup Settings", then click "Restart".
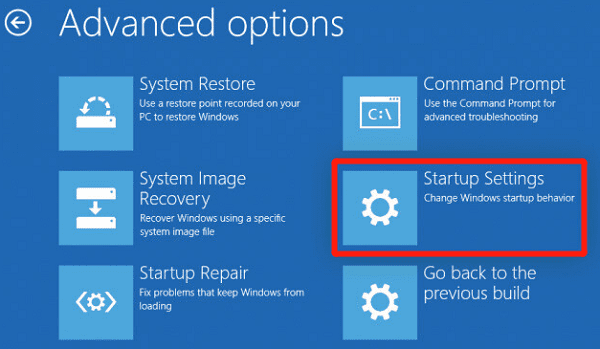
After restarting, press F4 to boot the computer into Safe Mode.
Run your computer in Safe Mode to see if it still crashes. If the crashes do not occur, the issue may be related to an installed application or driver.
4. Check Hard Drive
Run Disk Check Tool:
Open This PC, right-click on your system drive (usually C:), and select Properties.
Under the Tools tab, click "Check", then select Scan Drive.
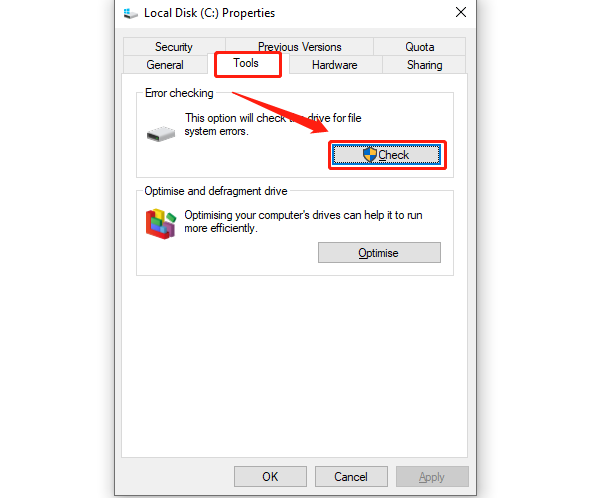
The system will scan and fix any errors on the hard drive. If any issues are found, the system will attempt to repair them.
Use Command Prompt to Repair Hard Drive:
Open Command Prompt (Admin), type "chkdsk /f", and press Enter.
The system will check the hard drive's file system and fix any detected errors.
Once completed, restart the computer and check if the issue is resolved.
5. Perform System Updates
Open Settings and click on "Update & Security".
Click "Check for Updates" to ensure the system has all the latest updates.
If updates are available, the system will automatically download and install them. After installation, restart the computer to ensure the updates take effect.
6. Repair System Files
Run System File Checker (SFC):
Open Command Prompt (Admin), type "sfc /scannow", and press Enter.
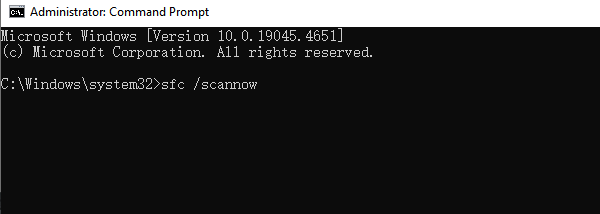
The system will automatically scan and repair any corrupted system files.
Run DISM Tool:
In Command Prompt (Admin), type the following command and press Enter:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
This tool will scan and repair the system's image files to help fix system file errors.
7. Run Windows Virus Scan
Open "Settings" > "Update & Security" > "Windows Security".
Select "Virus & Threat Protection", then click on "Quick Scan" or "Full Scan".
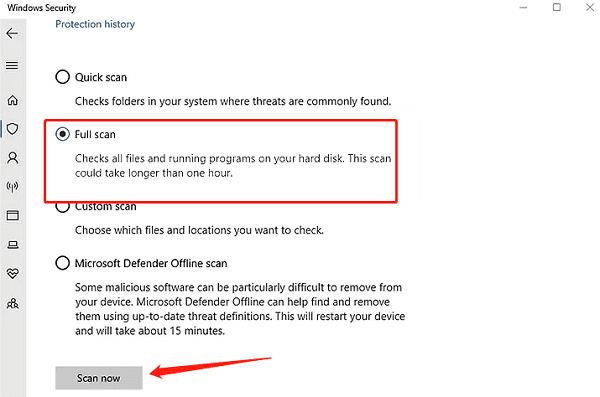
After the scan is complete, delete or quarantine any detected malware.
Once the virus scan is finished, restart your computer to check if the crash issue is resolved.
8. Perform System Restore
Open Control Panel and select "Recovery".
Click on "Open System Restore", then choose a restore point.
Follow the on-screen instructions, and the system will restore to the selected time point.
9. Ensure CPU is Functioning Normally
Open Driver Sentry, select the hardware section, and monitor the CPU temperature in real-time.
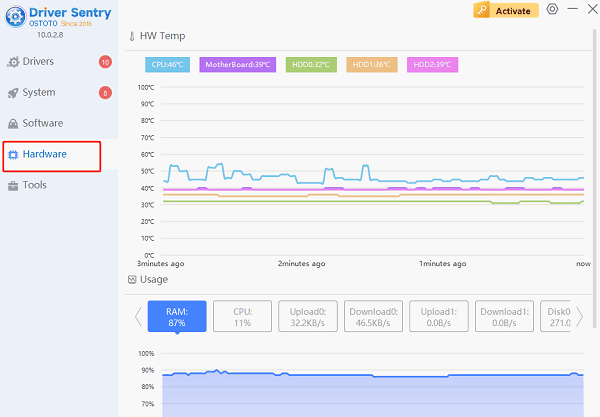
If the CPU temperature is too high (over 80°C), consider cleaning the cooler or replacing the fan.
Open Task Manager and check the CPU usage. If the CPU is under high load for an extended period, a process may be consuming too many resources, causing the system to crash.
Try ending high-load processes or uninstalling unnecessary software.
If the CPU is persistently overheating or not functioning properly, you may need to replace the CPU or conduct hardware diagnostics.
Following these steps can help you diagnose and fix Windows crash issues. If the problem persists, consider seeking professional technical support.
See also:
How to Fix the Keyboard Not Typing Issue
How to Fix Mouse Double-Click Issue